Courtesy of Sheep Genetics
Sheep Genetics implement annual analysis enhancements to ensure they continue to provide world-leading genetic evaluation services to clients. Sheep Genetics works alongside the Animal Genetics and Breeding Unit (AGBU) who are responsible for the research and development behind the enhancements to the Sheep Genetics evaluations.
In summary the enhancements implemented this year fall under 2 key themes:
There are more phenotypes and genotypes being used in the genetic evaluation than ever before, which enables new and updated ways for this data to be utilised.
The software used to develop indexes has undergone a major redevelopment to better model on-farm production systems and account for traits that will become important in breeding objectives in the future.
New Single Step Evaluation for Lambing Ease in LAMBPLAN for Terminals
Lambing ease (LE) is an important welfare and production efficiency trait. As such, lambing ease was introduced as an ASBV in 2007 and incorporated into Terminal indexes as part of the 2022 analysis enhancements.
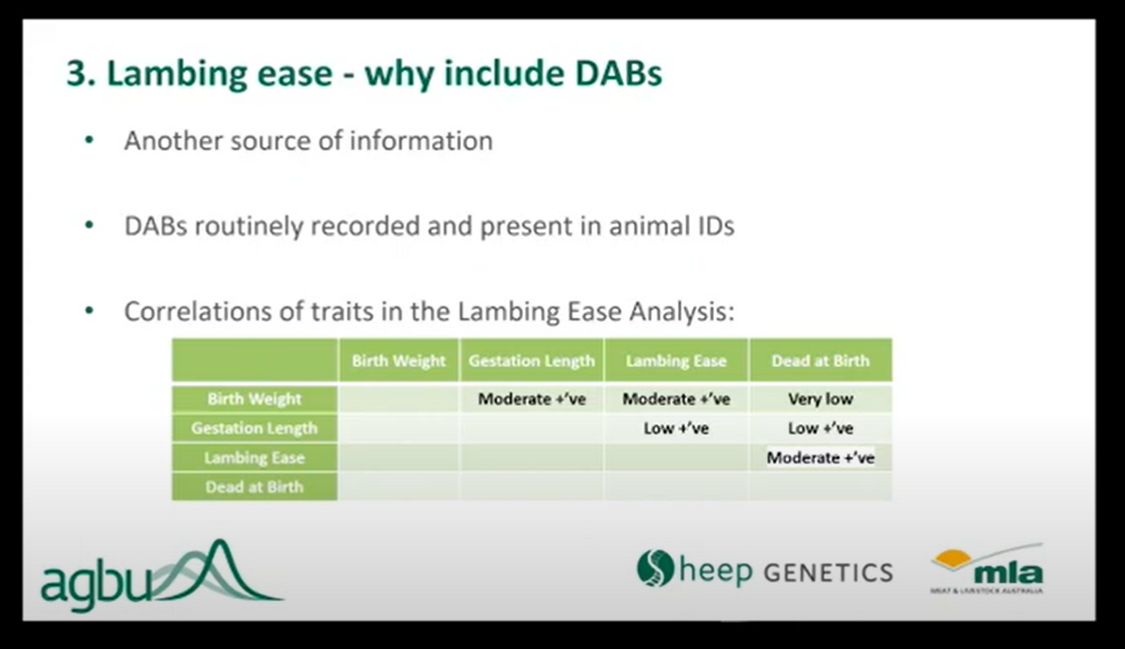
Currently, LE is a tri-variate analysis, meaning the analysis takes into account lambing ease score, birth weight, and gestation length when calculating ASBVs for lambing ease.
The analysis up until June 2023 does not use genomic information when calculating lambing ease ASBVs.
There are also efficiencies which can be made to this analysis to produce more accurate ASBVs in a timely manner.
Addition of dead at birth (DAB) data in the analysis model for lambing ease
As part of this year’s enhancements dead at birth (DAB) information supplied by breeders will be included in the model (along with lambing ease score, birth weight, and gestation length) to calculate lambing ease ASBVs.
Using DABs as a correlated trait in the lambing ease analysis improves the accuracy of the analysis.
Expression of variation in lambing ease in pure-bred flocks is a challenge. In the data supplied by breeders there is more expression of DAB and this information will be used to inform the calculation of LE ASBVs.
Moving Lambing Ease to a Single-Step Genomic model
Lambing ease was one of the only analysis models that did not use genomic information.
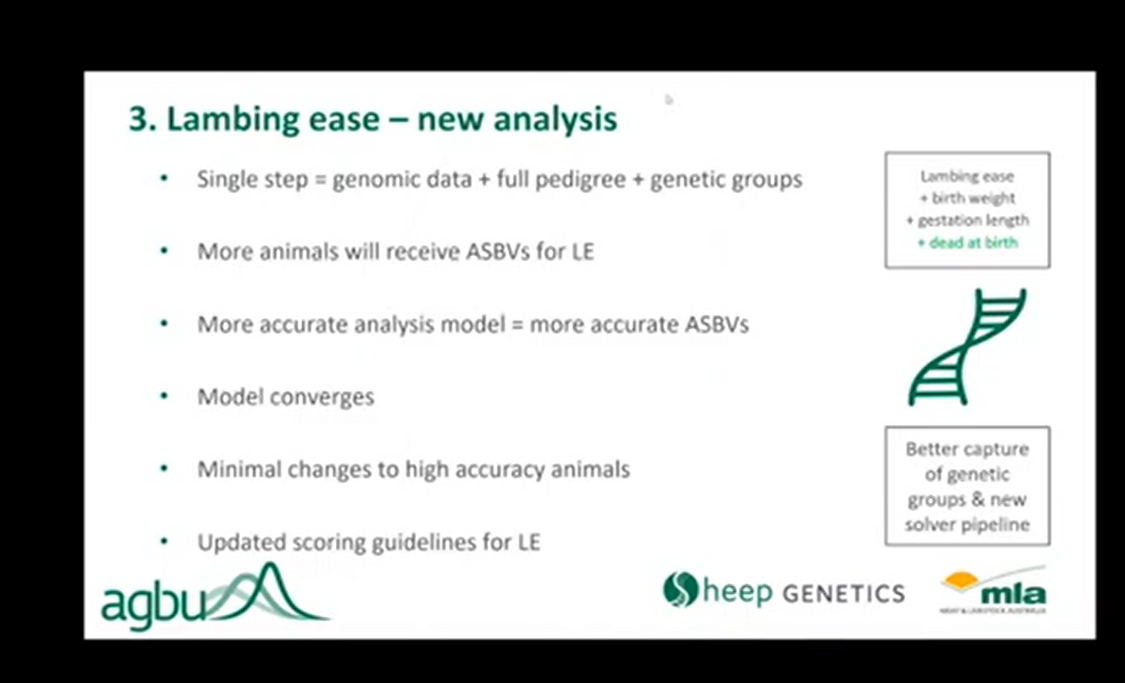
As part of the updates to the lambing ease analysis, a single step analysis model will now be used.
Single step evaluations use both trait measurement, pedigree relationships and genomic information.
Updating the lambing ease analysis to a single step model, and therefore the inclusion of genomic information and improved data filtering, will ensure increased accuracy of lambing ease ASBVs.
As a result more animals will receive a Lambing Ease ASBV.
What these enhancements mean for LE ASBVs:
The new model will result in increased in accuracy of lambing ease ASBVs.
There is a change in the genetic trend and the scale of the ASBVs. It will be important to look at the updated percentile bands from the analysis.
More animals will receive lambing ease ASBVs due to improved data filtering procedures.
Who is impacted?
Updating lambing ease to a single step model will mean more accurate ASBVs, as well as more animals receiving ASBVs for lambing ease.
There will be changes to the ASBVs and percentile ranking for Lambing Ease ASBVs.
Commercial measures of eating quality on Sheep Genetics animals
Sheep Genetics is working with breeders who are consigning SG animals to abattoirs, collecting commercial measures of eating quality. This applies to those who are processing animals that are in an SG evaluation and getting individual animal feedback for intra-muscular fat (from a probe or other device) and yield data (via DEXA). The intention is to investigate the relationship between these commercial measurements and the research measurements routinely taken in the MLA Resource Flock, to determine if commercial measures can be included in the genetic evaluation. If you have a consignment of animals that meets these requirements and are interested in being involved, please contact SG before the animals are consigned to ensure that all the necessary information is collected.
The below requirements are for breeders who are wanting to collect commercial carcase measurements;
Animals must have a Sheep Genetics ID and are in the Sheep Genetics evaluation (either excess animals from the stud or have pedigree information)
A pre-slaughter weight (4 hours fasted) on-farm prior to slaughter
Ideally pre-slaughter weight is to be recorded as soon as possible to the animals going onto the truck to slaughter, however, pre-slaughter measurements can be taken up to 7 days prior to slaughter
Date of pre-slaughter measurements
Management group of animals
Kill date and consignment number
Where possible, we recommend taking the following on farm pre-slaughter measurements also
Condition score
Fat and Muscle scan data